- Tech Insights 2025 Week 27by Johan Sanneblad
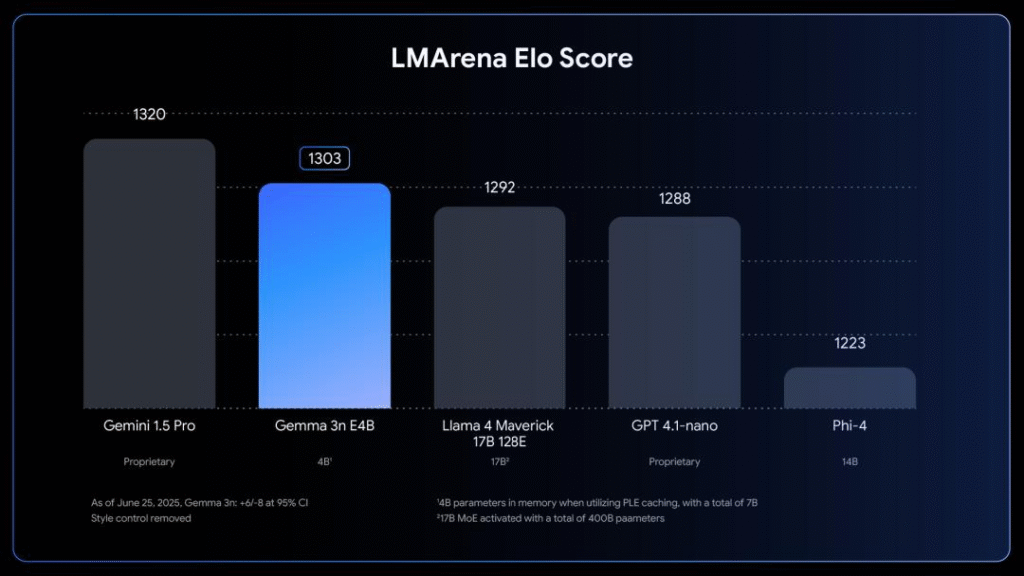
This was truly a week of edge and offline models releases! First Google released the full version of Gemma 3n, a multimodal AI model designed to run on edge devices with as little as 2GB of RAM. This means you can run it on smartphones or laptops without cloud connectivity, but the performance of it is truly outstanding! The small Gemma 3n 8B model (runs on 3GB RAM) is the first model under 10B parameters to score above 1300 points on LMArena, outperforming much bigger models like GPT 4.1-nano, Llama 4 Maverick 17B and Microsoft Phi-4. Gemma 3n is released free for commercial use, and Google even launched The Gemma 3n Impact Challenge with $150,000 in prizes to encourage developers to use the new model!
Google also released Gemini Robotics On-Device, a new model of Gemini Robotics with nearly identical performance to the cloud-based model, but can run fully locally. This is super interesting for any company working with industrial robots, and if you haven’t already contacted Google before you should probably do it now. Things are moving very quickly in this area.
Four weeks ago I first wrote about Black Forest Labs FLUX.1 Kontext, their amazing LLM that is able to change images using just text prompts, and compared to ChatGPT this one actually does a really good job changing images but also making them look the same as the original image. Last week Black Forest Labs launched FLUX.1 Kontext [dev], a 12-billion parameter model that runs fully local, without having to pay for API access! If you have an ad agency or a company working with lots of images, you should probably contact Black Forest Labs now to get pricing details.
And finally, Tencent released Hunyuan-A13B, a model you can run locally that is 80B parameters in size with only 13B parameters activated during inference, but is able to compete directly with DeepSeek R1 on benchmarks such as AIME 2025. A truly amazing model, but since it is not approved according to the AI Act it’s not possible to run it legally within the EU.
Listen to Tech Insights on Spotify: Tech Insights 2025 Week 27 on Spotify
Thank you for being a Tech Insights subscriber!
THIS WEEK’S NEWS:
- Google Releases Magenta RealTime Open-Source Music Generation Model
- Google Launches Doppl AI App for Virtual Outfit Try-Ons
- Google Releases Gemini CLI: Open-Source AI Agent for Terminal Development
- Google Releases Full Version of Gemma 3n Multimodal AI Model for Edge Devices
- Google Launches Imagen 4 Text-to-Image AI Model
- Google Releases Gemini Robotics On-Device Model for Offline Robot Operation
- Google DeepMind Releases AlphaGenome AI for DNA Sequence Analysis
- Anthropic Launches Interactive AI App Builder with No-Code Development
- Anthropic Introduces Desktop Extensions for One-Click MCP Server Installation
- Black Forest Labs Releases FLUX.1 Kontext [dev] Open-Weight Image Editing Model
- Inception Labs Launches Mercury, First Commercial Diffusion-Based Language Model
- Microsoft Introduces Mu: 330M Parameter On-Device Language Model for Windows Settings
- Tencent Open-Sources Hunyuan-A13B Language Model with Efficient MoE Architecture
Google Releases Magenta RealTime Open-Source Music Generation Model
https://magenta.withgoogle.com/magenta-realtime
The News:
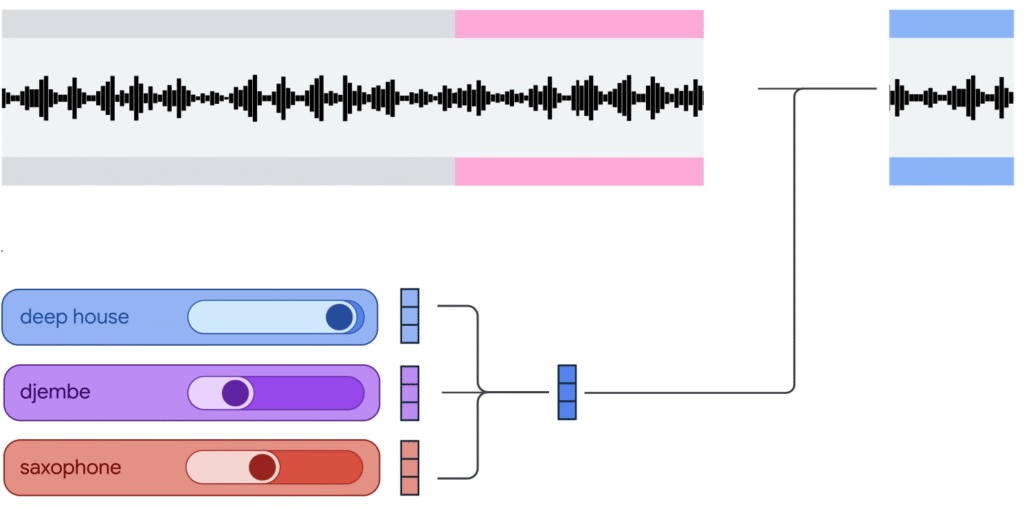
- Google released Magenta RealTime (Magenta RT), an open-weights AI model that generates music in real-time, allowing users to interactively create and control musical output during live performance or creative sessions.
- The model contains 800 million parameters and was trained on approximately 190,000 hours of instrumental stock music, primarily Western music.
- Magenta RT generates music in 2-second chunks based on the previous 10 seconds of audio context.
- Users can control the music by manipulating style embeddings through text prompts, audio examples, or weighted combinations of multiple prompts to blend different musical styles and instruments.
- The model outputs high-fidelity 48kHz stereo audio using SpectroStream codec and includes MusicCoCa, a joint music-text embedding system for better prompt understanding.
- Code is available on GitHub and model weights are distributed through Google Cloud Storage and Hugging Face under permissive licenses.
My take: Well here’s this weeks first “go watch this now” video. 😊 Seriously, go watch it, it’s just one minute. Magenta RealTime Colab Example – YouTube. Compared to existing models like MusicGen and MusicLM, Magenta RT differs by focusing on real-time generation rather than batch processing. Sure the 10 second context window can create limitations for longer music structures, but for real-time DJ-style mixing this is the closest we have seen so far to a DJ creating music on the fly. Since the model is fully open source with model weights published online, this could lead to some amazing new digital music instruments being released later this year.
Read more:
Google Launches Doppl AI App for Virtual Outfit Try-Ons
https://blog.google/technology/google-labs/doppl

The News:
- Google released Doppl, an experimental app from Google Labs that creates AI-generated images and videos showing how outfits look on users’ digital avatars, currently only available on iOS and Android in the US.
- Users upload a full-body photo of themselves and screenshots of any outfit from social media, thrift stores, or websites to generate virtual try-on images within minutes.
- The app converts static images into animated videos showing users wearing the outfits with poses like waving, smiling, or turning 360 degrees to simulate clothing movement.
- Doppl includes safety guardrails that block revealing outfits like swimwear and prevent uploads of public figures to avoid deepfake misuse.
- Google warns the experimental app “might not always get things right” with fit, appearance, and clothing details potentially inaccurate, particularly struggling with pants rendering and body proportions in mirror selfies.
My take: Here’s your second “go watch this now” video. Doppl is an experimental app from Google Labs and builds on their previous virtual try-on feature launched in May 2025 that only worked in Google search results. Releasing Doppl as a separate app expands this functionality to any online clothing source and also adds video animation features. Feedback from users have so far been very positive, with the only drawback being processing time that can take several minutes.
Read more:
- Doppl, a new experiment from Google Labs | Try on any look and explore your style – YouTube
- Google’s Doppl app took off my socks | The Verge
Google Releases Gemini CLI: Open-Source AI Agent for Terminal Development
https://blog.google/technology/developers/introducing-gemini-cli-open-source-ai-agent
The News:
- Google launched Gemini CLI, an open-source AI agent that brings Gemini 2.5 Pro directly into the terminal for coding, problem-solving, and task management.
- The tool offers free access with 60 model requests per minute and 1,000 requests per day, plus a 1 million token context window for handling large codebases.
- Users can authenticate with a personal Google account to get a free Gemini Code Assist license, or use API keys for higher usage limits.
- Gemini CLI supports Model Context Protocol (MCP) and integrates with Google Search, YouTube, and Drive.
My take: The past few weeks I have used over 2 trillion tokens in Claude Code, so when Google announced their own Claude Code competitor Gemini CLI with “free access” up to 60 requests per minute I rushed to install it! I started copying my CLAUDE.md to GEMINI.md in one of my repositories and asked Gemini CLI to read it, and then it immediately ran out of free tokens, disabled Gemini 2.5 Pro, and locked itself to Gemini 2.5 Flash. So yeah it’s free to use, but free in this case only means free access to Gemini 2.5 Flash, and I would never use that to develop anything that’s running on my computer. Free access to Gemini 2.5 Pro is limited to just a few tokens per day. Gemini CLI was also painfully slow, I tried using it with Gemini 2.5 Flash for a while but compared to Claude Code it was not really usable. I will give Gemini CLI a strong pass for now, and then maybe give it another go in 2-3 months if Google manages to improve the speed of it and changes their licensing terms and provides an unlimited Gemini 2.5 Pro usage model like Anthropic does with Claude Max.
Read more:
Google Releases Full Version of Gemma 3n Multimodal AI Model for Edge Devices
https://developers.googleblog.com/en/introducing-gemma-3n-developer-guide
The News:
- Google released the full version of Gemma 3n, a multimodal AI model designed to run on edge devices with as little as 2GB of RAM, enabling developers to deploy AI capabilities directly on smartphones, laptops, and low-end hardware without cloud dependencies.
- The model natively processes images, audio, video, and text inputs while generating text outputs, supporting 140 languages for text and multimodal understanding across 35 languages.
- Available in two sizes based on “effective parameters”: E2B (5B parameters, runs on 2GB RAM) and E4B (8B parameters, runs on 3GB RAM), with actual memory usage equivalent to traditional 2B and 4B parameter models through architectural optimizations.
- Google also launched The Gemma 3n Impact Challenge with $150,000 in prizes to encourage developer adoption and innovation using the new model.
My take: The Gemma 3n E4B model became the first model under 10 billion parameters to exceed 1300 points on LMArena, outperforming larger models like Llama 4 Maverick 17B, GPT 4.1-nano, and Phi-4. The model uses the MatFormer architecture (🪆 Matryoshka Transformer) which allows a single model to run at different sizes for different tasks, similar to Russian nesting dolls, providing flexibility that other providers typically achieve through separate model variants. This is a super interesting model and an amazing achievement by Google, so if you are interested in AI models and AI engineering, grab a cup of coffee and go read [Introducing Gemma 3n: The developer guide](# Introducing Gemma 3n: The developer guide), it’s very well written and mandatory reading for anyone working with AI development.
Read more:
- Google – The Gemma 3n Impact Challenge | Kaggle
- Introducing Gemma 3n: The developer guide – Google Developers Blog
- [2310.07707] MatFormer: Nested Transformer for Elastic Inference
Google Launches Imagen 4 Text-to-Image AI Model
https://developers.googleblog.com/en/imagen-4-now-available-in-the-gemini-api-and-google-ai-studio

The News:
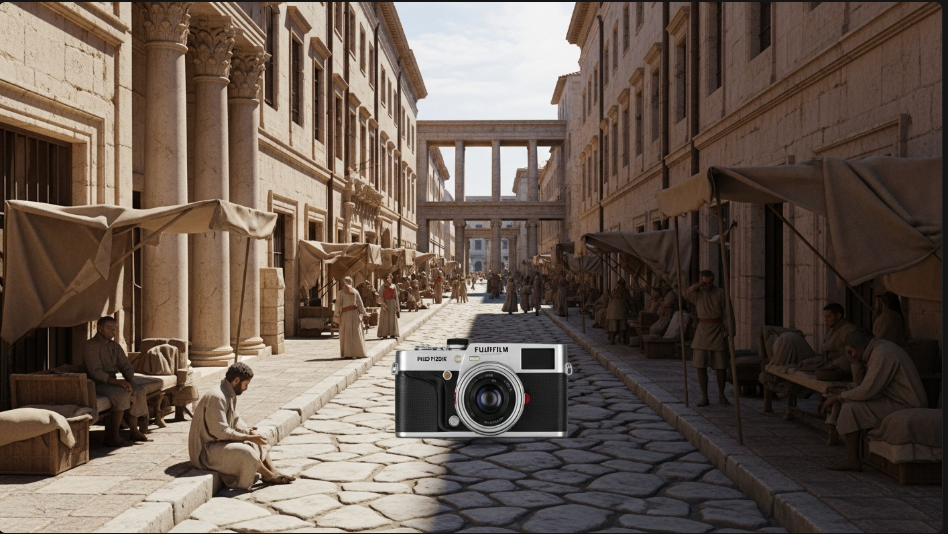
- Google released Imagen 4, its latest text-to-image AI model, through the Gemini API and Google AI Studio. The model generates images from text prompts and offers improved text rendering capabilities compared to Imagen 3.
- Two versions are available: standard Imagen 4 at $0.04 per image for general use, and Imagen 4 Ultra at $0.06 per image for more precise prompt following and higher alignment with user instructions.
- The model shows enhanced performance in detailed close-ups, complex scenes with multiple elements, and text generation within images. Google reports generation speeds up to 10x faster than Imagen 3.
- Access is currently limited to paid preview in Gemini API and free testing in Google AI Studio, with general availability planned for coming weeks.
My take: Google Imagen 4 is still not open for general availability, and if you decide to try it out for yourself you quickly see why. Sometimes you are lucky and get quite good results, other times it completely misunderstands your prompt, like the example above “Ancient Roman Street Scene, Fujifilm X100F, 50mm” (where it drew an ancient street and then just pasted the camera in front of it, instead of showing a photo shot with the camera). Unless you really have the need for a new image generator give this one a strong pass for now and go use something like FLUX.
Read more:
Google Releases Gemini Robotics On-Device Model for Offline Robot Operation
https://deepmind.google/discover/blog/gemini-robotics-on-device-brings-ai-to-local-robotic-devices
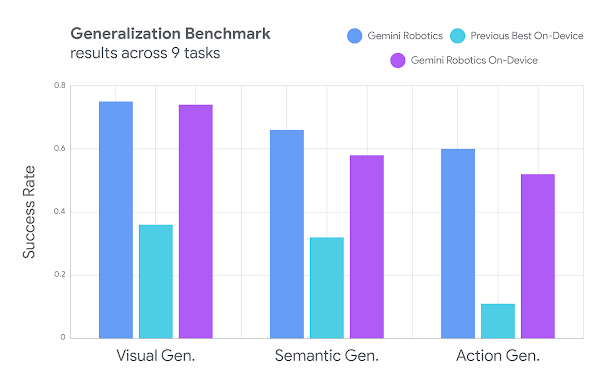
The News:
- Google DeepMind launched Gemini Robotics On-Device, a vision-language-action model that runs locally on robots without internet connectivity, eliminating cloud dependency for robotic operations.
- The model performs complex dexterous tasks like unzipping bags, folding clothes, and pouring salad dressing while operating entirely offline with low-latency inference.
- Robots can adapt to new tasks using just 50 to 100 demonstrations, showing strong generalization across unfamiliar objects and multi-step instructions.
- Google tested the model on seven manipulation tasks of varying difficulty, including zipping lunchboxes and drawing cards, where it outperformed existing on-device models after fine-tuning.
- While originally trained on Google’s ALOHA robot, the model successfully adapted to other platforms including the bi-arm Franka FR3 robot and Apptronik’s Apollo humanoid robot.
My take: In Tech Insights Week 12 I reported about Gemini Robotics, where Google equipped their Gemini 2.0 model with hands to bring Gemini’s multimodal reasoning and real-world understanding into the physical world. Now Google is introducing Gemini Robotics On-Device, which runs Gemini Robotics locally with low-latency inference. It kind of makes you wonder though what hardware is required to run this thing, looking at the benchmarks it performs nearly as good as the full connected Gemini Robotics model. Google does not disclose anything about this, other than it has been “engineered to require minimal computational resources”, whatever that means. So until Google discloses exactly what hardware is required to make this model run as good as it is (a stack of H200 cards, who knows?) don’t get too excited about having your standard industry robots becoming smart over night.
Read more:
Google DeepMind Releases AlphaGenome AI for DNA Sequence Analysis
https://deepmind.google/discover/blog/alphagenome-ai-for-better-understanding-the-genome
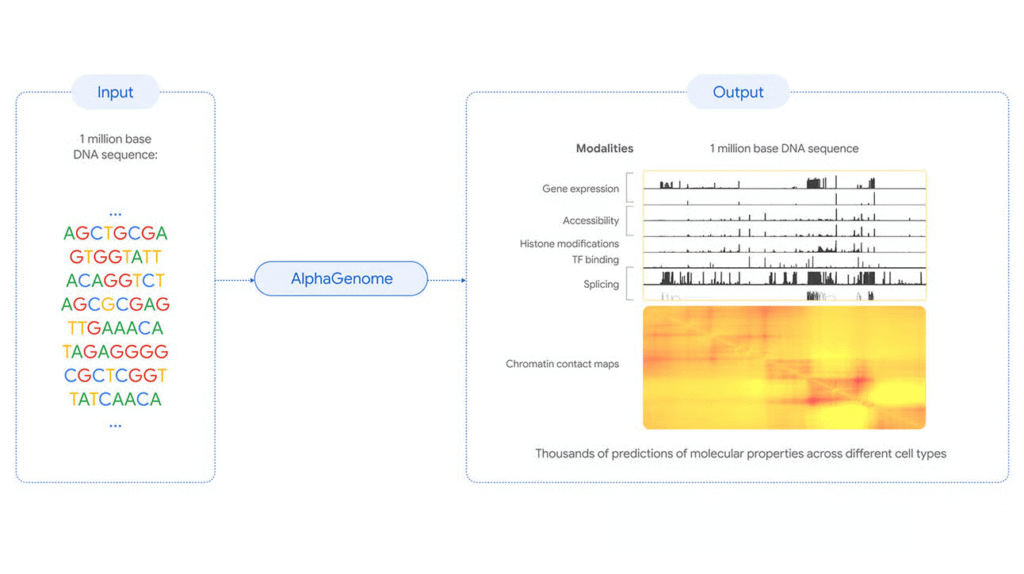
The News:
- Google DeepMind launched AlphaGenome, an AI model that predicts how genetic variants affect molecular processes in human DNA sequences, helping researchers understand the 98% of the genome that doesn’t code for proteins but regulates gene activity.
- The model analyzes DNA sequences up to 1 million base pairs long and makes predictions at single-base resolution across thousands of molecular properties, including gene expression levels, RNA splicing patterns, and protein-DNA binding sites.
- AlphaGenome outperformed existing models in 22 out of 24 single-sequence benchmarks and 24 out of 26 variant-effect prediction tasks, demonstrating superior performance across multiple genomic analysis categories.
- The system can score genetic variant impacts within one second by comparing mutated versus unmutated sequences, enabling rapid analysis of thousands of genetic variations found in disease studies.
- AlphaGenome is the first model to directly predict RNA splice junction positions and expression levels from DNA sequences, relevant for understanding rare diseases like spinal muscular atrophy and cystic fibrosis.
My take: It has now been nearly 25 years since researchers completed a draft of the human genome sequence, but still many of its 3.1 billion letters remain a puzzle. Especially the 98% of the genome that is not made of protein-coding genes, but can influence their activity, is very much unexplored. According to Google’s head of AI for science, Pushmeet Kohli, “This is one of the most fundamental problems not just in biology – but in all of science”. Researchers at Palo Alto who have had early access to AlphaGenome say that “it is a genuine improvement in pretty much all current state-of-the-art sequence-to-function models”, and “an exciting leap forward”. And while it widely exceeds previous models for benchmarks and tasks in the same domain, it’s still very much a stepping stone with little practical use today.
Read more:
Anthropic Launches Interactive AI App Builder with No-Code Development
https://www.anthropic.com/news/claude-powered-artifacts
The News:
- Anthropic introduced a beta feature allowing Claude users to build, host, and share interactive AI-powered apps directly within the chatbot interface, expanding beyond static content creation to functional applications.
- Users describe their app idea in natural language and Claude generates the complete code, handles hosting, and provides instant sharing through links without requiring coding knowledge or deployment processes.
- Apps can integrate Claude’s API functionality, enabling dynamic features like personalized tutoring systems, data analysis tools that process uploaded CSV files, and AI-powered games with adaptive NPCs that remember player interactions.
- The cost structure passes API usage to app users rather than creators – when someone uses your app, they authenticate with their existing Claude account and their usage counts against their subscription, eliminating the need for API key management.
- Early adopters have created educational tools that adjust to individual skill levels, writing assistants for technical documentation, and agent workflows that coordinate multiple Claude API calls for complex tasks.
My take: Last year Anthropic released Artifacts, which allowed code generation and visualization but was limited to static content. This AI App Builder directly competes with OpenAI’s ChatGPT Canvas, though Claude’s approach differs by enabling full app hosting and API integration within the platform itself. User feedback has so far been very positive, and if you have a minute here’s your third video of the week to watch.
Read more:
Anthropic Introduces Desktop Extensions for One-Click MCP Server Installation
https://www.anthropic.com/engineering/desktop-extensions
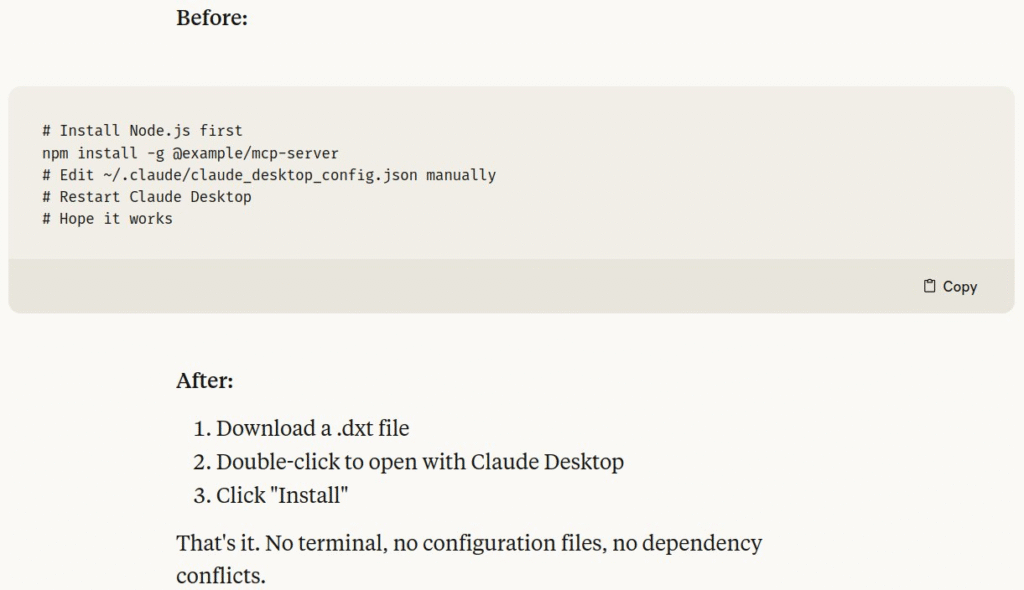
The News:
- Anthropic launched Desktop Extensions (.dxt files), a new packaging format that simplifies installing Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers for Claude Desktop users by eliminating complex manual setup processes.
- The system bundles entire MCP servers with all dependencies into single installable packages, reducing installation from multi-step terminal commands to downloading a .dxt file and clicking “Install”.
- Extensions include built-in Node.js runtime, automatic updates, and secure storage of API keys in the OS keychain, removing requirements for users to install developer tools or edit JSON configuration files.
- Anthropic open-sourced the complete DXT specification, packaging tools, and reference implementation code to enable other AI applications to support the format.
- The company launched with a curated extension directory built into Claude Desktop and provides enterprise features including Group Policy support, extension blocklists, and private directory deployment.
My take: Installing local MCP servers was previously way too complicated for the average user, so this makes a huge difference for MCP adoption. Just download a .DXT file, double click to open it with Claude Desktop, click “Install”, and you are done! There are so many exciting possibilities opening up with MCP for both local and remote servers, and this is the main reason I use Claude more than I use ChatGPT today. The new DXT standard also supports automatic updates, so extensions will update automatically when new versions are available. If you haven’t yet gotten started with MCP you should really spend a few minutes just checking out what’s available and how you can use it.
Read more:
- Local MCP servers can now be installed with one click on Claude Desktop : r/ClaudeAI
- GitHub – wong2/awesome-mcp-servers: A curated list of Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers
Black Forest Labs Releases FLUX.1 Kontext [dev] Open-Weight Image Editing Model
https://bfl.ai/announcements/flux-1-kontext-dev

The News:
- Black Forest Labs released FLUX.1 Kontext [dev], a 12-billion parameter open-weight image editing model that runs on consumer hardware and matches proprietary-level performance for non-commercial use.
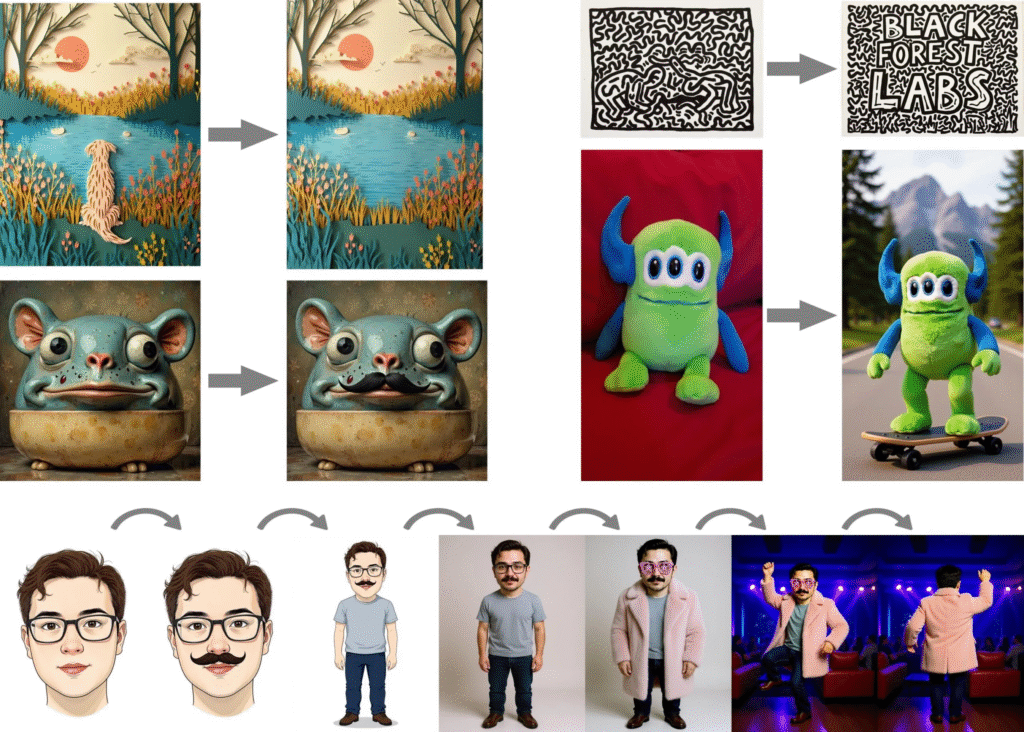
- The model focuses exclusively on image editing tasks rather than text-to-image generation, enabling iterative editing while preserving character consistency across different scenes and environments.
- FLUX.1 Kontext [dev] supports both local and global edits, style transfer, text modification within images, and multi-step editing workflows without quality degradation.
- The model runs at speeds of 6-10 seconds per generation and is compatible with existing FLUX.1 [dev] inference code, with day-0 support for ComfyUI, HuggingFace Diffusers, and TensorRT.
- Commercial licenses for the open weights models can now be purchased directly, while the dev version remains free for research and non-commercial use under the FLUX.1 Non-Commercial License.
My take: If you ever tried to send an image to ChatGPT and ask it to change a thing or two, you most probably found out that the resulting imagediffered greatly from the original image. This is where FLUX.1 Kontext shines. Send in any image, tell it what you need to be changed, and the resulting image will be extremely close to the source image, changing only the sections you asked from it. I wrote about FLUX.1 Kontext in Tech Insights 2025 Week 23, and now Black Forest Labs released FLUX.1 Kontext [dev] with the main difference that it can run locally without cloud connections. This also means that you do not pay for API usage with this model. You can use it for free for non-commercial uses, and for commercial use cases you need to contact Black Forest Labs directly.
Inception Labs Launches Mercury, First Commercial Diffusion-Based Language Model
https://www.inceptionlabs.ai/introducing-mercury-our-general-chat-model
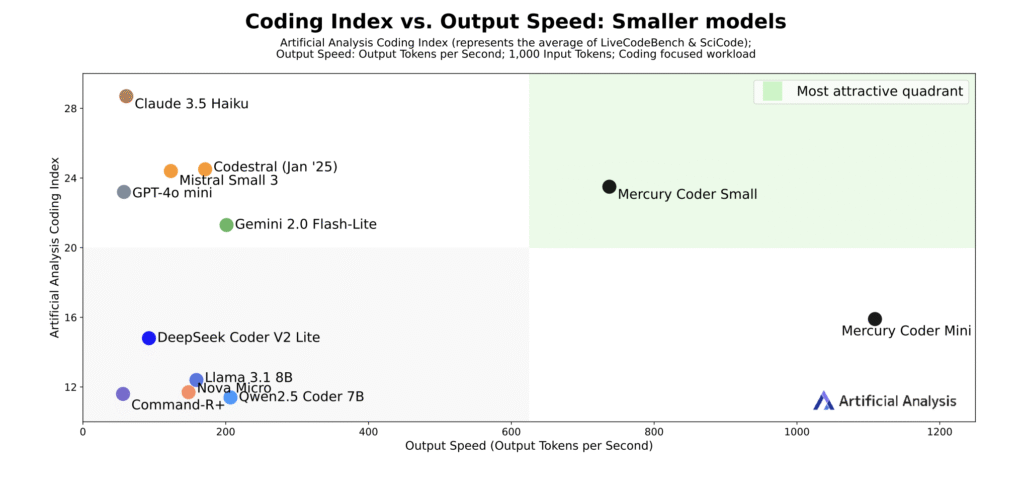
The News:
- Inception Labs released Mercury, the first commercial-scale diffusion-based large language model designed for chat applications, offering significantly faster text generation than traditional transformer-based models.
- Mercury generates text using a “coarse-to-fine” diffusion process that creates all tokens simultaneously rather than sequentially, achieving over 1,000 tokens per second on NVIDIA H100 GPUs.
- The Mercury Coder Mini version reached 1,109 tokens per second in testing, while Mercury Coder Small achieved 737 tokens per second.
- Independent testing by Artificial Analysis shows Mercury runs 10 times faster than current advanced models while matching the performance of speed-optimized frontier models like GPT-4o Mini and Claude 3.5 Haiku.
- Several Fortune 500 companies are testing Mercury for customer support chatbots, though the company declined to name specific clients.
- The model includes fine-tuning capabilities and software infrastructure for business deployment, with a free testing version available.
My take: All major language models today use what is called an autoregressive approach. Where autoregressive models like ChatGPT generate text one word at a time in sequence, diffusion models generate entire responses simultaneously by starting with random noise and refining the complete text through multiple passes, delivering significantly faster performance at lower computational costs. Mercury is still no match for larger models in performance, but compared to smaller models, Mercury Coder Small scored 90.0% on HumanEval compared to GPT-4o Mini’s 88.0% and Claude 3.5 Haiku’s 86.0%, while running significantly faster at 737 tokens per second versus their 59-61 tokens per second. If you want to give it a try you can test it for free at their playground, and if you want to start testing it through their API you can sign up at their web site. Being able to match GPT-4o Mini in performance but being almost 10 times faster is reason enough to be excited about diffusion models, so I will keep an eye out for improvements in this area going forward.
Read more:
- Mercury Playground
- Diffusion Models Enter the Large Language Arena as Inception Labs Unveils Mercury
Microsoft Introduces Mu: 330M Parameter On-Device Language Model for Windows Settings
The News:
- Microsoft released Mu, a 330 million parameter encoder-decoder language model that runs entirely on Neural Processing Units (NPUs) in Copilot+ PCs to power a natural language agent in Windows Settings.
- The model achieves over 100 tokens per second response speed and completes Settings queries in under 500 milliseconds, running fully offline without sending data to Microsoft servers.
- Mu delivers 47% lower first-token latency and 4.7 times faster decoding speed compared to decoder-only models of similar size on Qualcomm Hexagon NPUs.
- Microsoft trained the model on 3.6 million samples covering hundreds of Windows settings, using synthetic data generation and fine-tuning techniques to handle diverse user queries.
My take: Traditional control queries such as “increase sound” and “turn off Bluetooth” can easily be solved with traditional Machine Learning, but when users describe problems like “It feels like my windows lag behind when I move them around my screen” you need a transformer-based model to guess that it might be related to the refresh rate of the monitor. Microsoft Mu achieves performance nearly comparable to Phi-3.5-mini despite being one-tenth the size, which is super amazing. This is probably the way we will use LLMs in our operating systems going forward – small, local, and specialized models built for specific purposes, and with recent achievements such as Mu and Gemma 3n these small models are way more capable than we could have ever imagined just a year ago.
Read more:
Tencent Open-Sources Hunyuan-A13B Language Model with Efficient MoE Architecture
https://github.com/Tencent-Hunyuan/Hunyuan-A13B
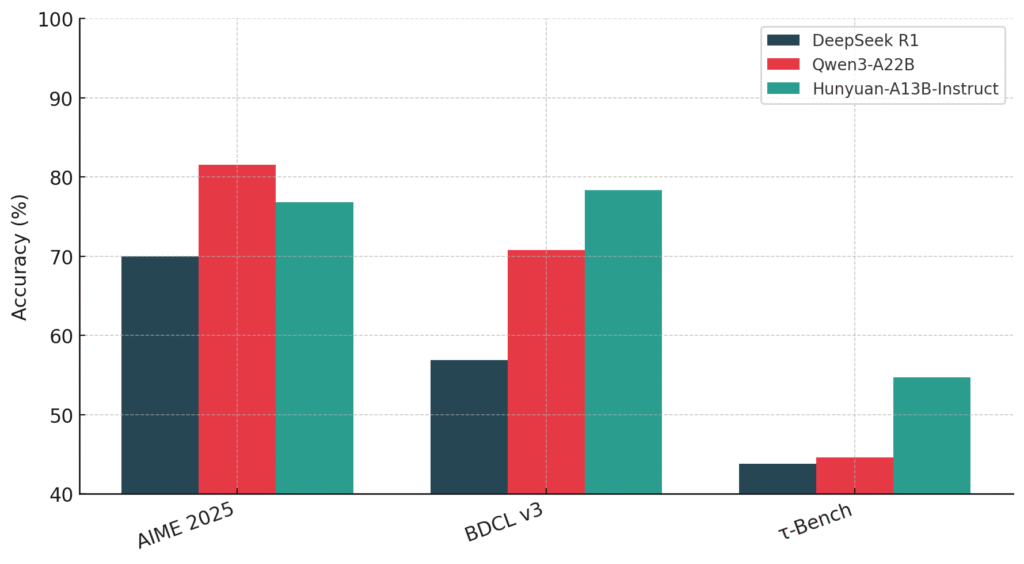
The News:
- Tencent released Hunyuan-A13B, an open-source large language model that uses a Mixture-of-Experts architecture to deliver high performance while requiring significantly fewer computational resources than traditional models.
- The model contains 80 billion total parameters but activates only 13 billion during inference, reducing memory requirements and computational costs while maintaining competitive performance.
- The model offers dual reasoning modes: fast thinking for immediate responses and slow thinking for deeper analytical processing, allowing users to balance speed and accuracy based on their needs.
- Performance benchmarks show the model achieving 87.3 on AIME 2024 mathematics tests and 78.3 on BFCL v3 agent capabilities, competing closely with larger models like DeepSeek R1.
- Tencent also open-sourced two evaluation datasets: ArtifactsBench with 1,825 coding tasks and C3-Bench with 1,024 agent scenario tests.
My take: If you live outside the UK, EU and South Korea this is a very interesting model if you want to run models locally and have the hardware to do it. 80 billion parameters means the model will easily run on a Mac Studio 128GB machine at 8-bit quantization, and having only 13 billion parameters activated during inference means it should be much faster than anything else with this performance. The model outperforms Qwen3-32B across all benchmarks and nearly matches Qwen3-A22B performance while activating 40% fewer parameters. The licensing agreement prevents it from being run within the EU, UK and South Korea, so if you live here then just move along, this model is not for you.
Read more: